The Quest to Tame NASA Supersonic Shockwaves
For a long time, the crackling increase of a supersonic plane has been a symbol of velocity and technological prowess. However, these sonic booms have also been the bane of populated regions near flights. Take a look at ranges. The exquisite noise generated through supersonic flight has led to strict rules and restrictions. Enter NASA’s groundbreaking research into supersonic shockwaves, which seeks to revolutionize the destiny of aviation and open up the skies to faster, quieter, and more efficient travel. In this text, we delve into NASA’s quest to tame supersonic shockwaves and the capability it holds for the aviation industry.
The quest to tame NASA’s supersonic shockwaves represents a pioneering undertaking in the realm of aerospace. Supersonic flight has long been marred by the disruptive and ear-splitting sonic booms that result from planes breaking the sound barrier. NASA’s ongoing efforts to mitigate those shockwaves maintain the promise of revolutionizing air travel.
By growing revolutionary aircraft designs and modern technology, which include the Quiet Supersonic Technology (QueSST) task, NASA aims to create a brand new technology of supersonic planes that produce quieter, more desirable sonic thumps. This undertaking now not only best addresses the sonic growth issue but also paves the way for a future where the supersonic journey will become a viable and more environmentally friendly choice.
Ultimately, the search to tame NASA’s supersonic shockwaves exemplifies the enterprise’s dedication to pushing the limits of aviation, making air travel faster, quieter, and more sustainable for generations to come.
The Sonic Boom Conundrum
NASA faces the sonic growth conundrum head-on because it strives to revolutionize the supersonic tour. For many years, the disruptive and thunderous shockwaves produced by planes breaking the sound barrier had been a major impediment to the return of business supersonic flight. NASA’s pursuit of mitigating these sonic booms is an ambitious and multidimensional project that involves contemporary aerodynamics, computational modeling, and enormous flight testing.
By specializing in superior aircraft designs and using revolutionary technologies, which include the X-59 QueSST (Quiet Supersonic Technology) plane, NASA seeks to reshape the future of aviation. The aim is to create supersonic aircraft that generate sonic thumps quiet enough not to disturb ground communities, potentially ushering in an era in which excessive-velocity air travel becomes possible without the annoyance of deafening sonic booms.
In tackling the sonic boom conundrum, NASA exemplifies its dedication to advancing aerospace technology and era, aiming to make the supersonic journey more sustainable, green, and harmonious with the sector.
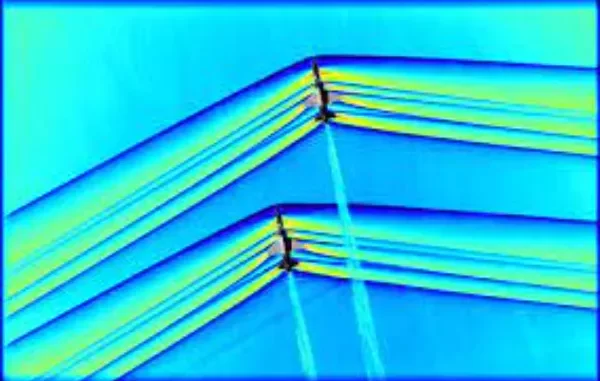
Supersonic flight, described as flying quicker than the velocity of sound (about 767 miles per hour or 1,235 kilometers per hour at sea level), has long been a fascination of aerospace engineers and fans. However, this fascination came with a significant downside: sonic growth. As an aircraft exceeds the rate of sound, it generates shockwaves that coalesce right into an effective strain wave, resulting in the characteristic sonic growth heard at the ground.
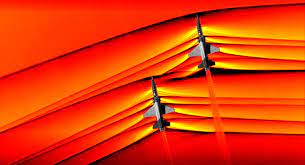
These sonic booms are disruptive, causing soreness and annoyance to those on the ground. As a result, supersonic flight over land is basically prohibited, restricting the software of the supersonic plane to overwater routes. This obstacle has hindered the improvement of business supersonic tours for decades.
NASA’s X-59 QueSST: A Game-Changer
In an effort to address the sonic growth problem, NASA initiated the Quiet Supersonic Transport (QueSST) application, which led to the improvement of the X-fifty-nine QueSST plane. This sleek, experimental aircraft is designed to fly at supersonic speeds while producing a sonic “thump” instead of a loud, disruptive boom. The purpose is to make this thump quiet enough to no longer disturb human beings on the ground.
NASA’s X-59 QueSST (Quiet Supersonic Technology) is poised to be a game-changer in the world of aviation. This experimental plane represents a groundbreaking step toward revitalizing commercial supersonic flight. The X-59 is designed with a unique form that minimizes the shockwaves produced at some stage in supersonic flight, correctly reducing the function of sonic booms to a mild thud, or sonic “heartbeat.”
This innovation holds the potential to reshape the aviation industry, as it promises to make supersonic travel extra acceptable, both in terms of noise pollution and environmental impact. By pioneering quieter supersonic aircraft generation, NASA aims to open doorways to quicker and more efficient air travel while addressing the historic challenge of sonic booms.
The X-59 QueSST embodies NASA’s determination to advance aerospace generation, and its success in development and testing could mark a considerable milestone in the adventure towards a greater available and sustainable future for high-pace air travel.
The X-fifty-nine QueSST Incorporates Numerous Progressive Design Features to Achieve This Aim:
The X-Fifty Nine QueSST incorporates several progressive design functions to achieve its groundbreaking aim of reducing sonic booms through supersonic flight. At the center of its innovative layout is a sleek and elongated form that minimizes the shockwaves generated as the aircraft travels faster than the speed of sound.
This specific design, often known as a “long, narrow frame,” allows the X-59 to distribute and weaken the shockwaves, resulting in a softer sonic thump as opposed to the loud, disruptive booms commonly associated with supersonic travel. The aircraft features a single-pilot cockpit with an ahead-facing windowless cabin, counting on superior camera structures to provide the pilot with a panoramic view, in addition to changing the form of design elements that would contribute to noise generation.
The integration of those contemporary design capabilities showcases NASA’s determination to push the boundaries of aerospace engineering and marks an extensive step closer to a quieter and more sustainable technology of supersonic air travel.
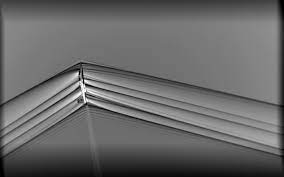
- Nose Design: The plane’s lengthy, narrow nose and thoroughly formed wings generate shockwaves that have interaction in a manner that substantially reduces their intensity.
- Boom Mitigation Systems: Onboard instrumentation and computational fashions continuously reveal and regulate the plane’s flight direction to reduce sonic boom depth.
- Quiet Cockpit: Advanced soundproofing and noise-canceling technology create extra-fine surroundings for pilots for the duration of supersonic flight.
Testing and Development
The testing and improvement of the X-59 QueSST represent an essential segment in NASA’s bold task to transform supersonic air travel. Extensive studies, rigorous simulations, and wind tunnel testing have played a pivotal role in refining the aircraft’s layout to achieve its number one aim—minimizing the impact of sonic booms.
These tests have allowed engineers and scientists to quality-track the plane’s shape, aerodynamics, and average performance to make sure it may efficaciously lessen shockwaves and create the desired sonic “heartbeat.” The X-Fifty Nine’s adventure also consists of a series of flight assessments, with NASA collaborating carefully with the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) to collect facts, data, and public feedback on noise levels generated by the plane’s sonic thump.
The efforts are instrumental in setting up new noise standards for supersonic travel and addressing regulatory hurdles. Through meticulous tests, development, and improvement, the X-Fifty Nine QueSST emerges as a testament to NASA’s commitment to revolutionize supersonic aviation, promising a future wherein quieter and more environmentally pleasant high-speed air travel will become a reality.
NASA’s X-59 QueSST has undergone rigorous checking, which includes wind tunnel critiques and check flights to acquire records on its sonic characteristics. The aircraft is part of NASA’s Low-Boom Flight Demonstrator (LBFD) program, which aims to illustrate the viability of quiet supersonic flight and pave the way for regulatory adjustments that would permit overland commercial supersonic travel.
The Future of Supersonic Flight
The future of NASA supersonic flight is a compelling, imaginative, and prescient vision of faster, quieter, and more environmentally sustainable air travel. Building on the improvements and advancements made through project models like the X-Fifty Nine QueSST, NASA has goals to revolutionize the aviation industry. By reducing the disruptive sonic booms associated with supersonic flight, NASA not only seeks to make high-speed travel extra socially applicable but also more available.
The instructions discovered from the X-Fifty Nine software will describe the improvement of new-era supersonic business aircraft, possibly opening up new markets and opportunities for airlines and tourists. NASA’s cognizance of sustainability means that those future supersonic aircraft may also comprise greener technologies and more fuel-efficient engines, aligning with international efforts to lessen the environmental impact of aviation.
In essence, the future of NASA supersonic flight holds the promise of transforming the way in which we travel, supplying a compelling vision of high-velocity air travel that isn’t always the simplest or fastest but also more responsible and in accordance with the needs of our changing world.
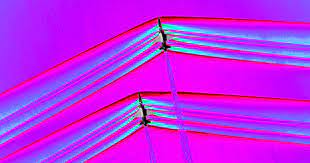
The success and improvement of the X-fifty-nine QueSST hold the promise of a brand new technology for supersonic aviation. NASA’s studies and innovation ought to cause a fundamental shift in how we understand and alter supersonic flight. If rules are revised to deal with quieter supersonic aircraft, we could see a resurgence in commercial supersonic journeys, considerably decreasing journey instances for long-haul flights.
Conclusion on the NASA Supersonic Shockwaves
In the end, NASA’s pioneering efforts to tame supersonic shockwaves constitute an exceptional journey of innovation and discovery. Through rigorous research, testing, and the improvement of present-day technology, NASA has strived to convert the area of supersonic flight.
The fulfillment of projects like the X-Fifty Nine QueSST has now not only addressed the longstanding issue of disruptive sonic booms but has also opened the door to a future where supersonic air travel may be faster, quieter, and more environmentally friendly.
This project demonstrates NASA’s unwavering commitment to advancing aerospace technological know-how and technology while implementing sustainable and responsible aviation practices. The legacy of NASA’s work on supersonic shockwaves is one of development, promise, and the relentless pursuit of pushing the bounderies of human travel and success in the skies above.
NASA’s pioneering work on taming supersonic shockwaves isn’t always pretty much about making air travel faster; it’s also about making it more accessible and sustainable. By addressing the longstanding problem of sonic booms, NASA’s X-fifty-nine QueSST represents a large jump forward in the future of aviation. As the plane continues to undergo checking out and refinement, it brings us closer to an international wherein supersonic flight is not just the stuff of dreams but a realistic and green mode of transportation. With NASA’s relentless pursuit of innovation, the skies may additionally soon be open to a brand new era of supersonic tour that redefines how we discover our planet.






Leave a Reply